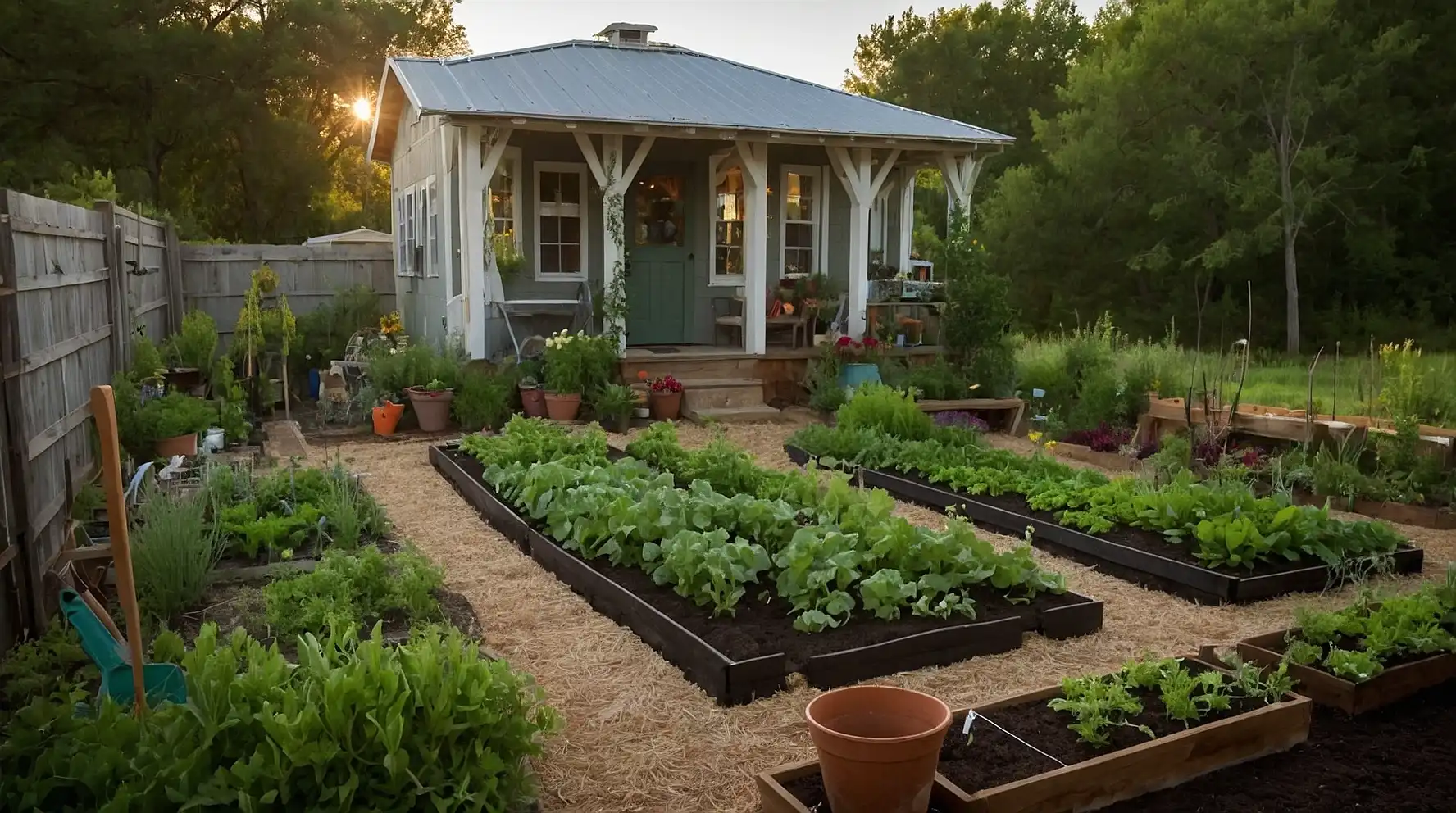
27 Homesteading Garden Layout Ideas
Your homestead garden layout determines how efficiently you can grow food while minimizing work and maximizing yields.
Smart design creates sustainable systems that support self-sufficient living.
These proven layout strategies help you organize crops, manage resources, and plan for year-round production.
You’ll discover approaches that work with nature rather than against it.
Transform your growing space into a productive homestead that feeds your family while building soil health and supporting beneficial wildlife.
1: Raised Bed Grid System Organization
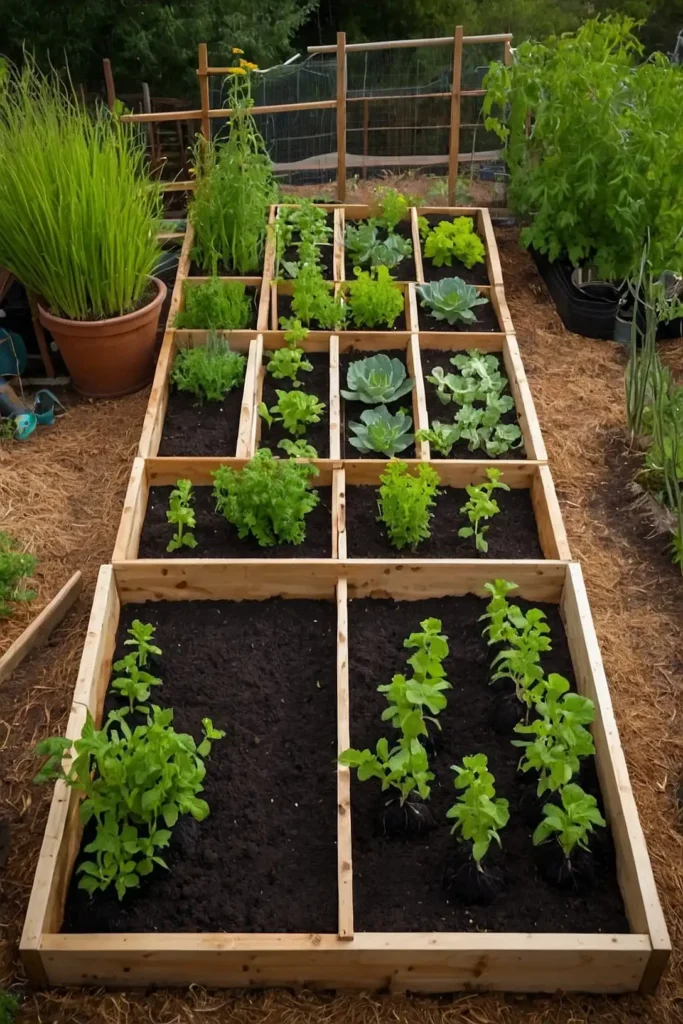

Create a systematic grid of raised beds that maximizes growing space while providing easy access for maintenance and harvesting.
You’ll improve soil drainage while establishing clear pathways between organized growing areas.
Build beds 4 feet wide so you can reach the center from either side comfortably.
This width prevents soil compaction while allowing intensive planting in well-defined spaces.
Leave 2-3 feet between beds for wheelbarrow access and comfortable walking paths.
The organized approach simplifies crop rotation while creating a professional, manageable garden layout.
2: Companion Planting Zone Design
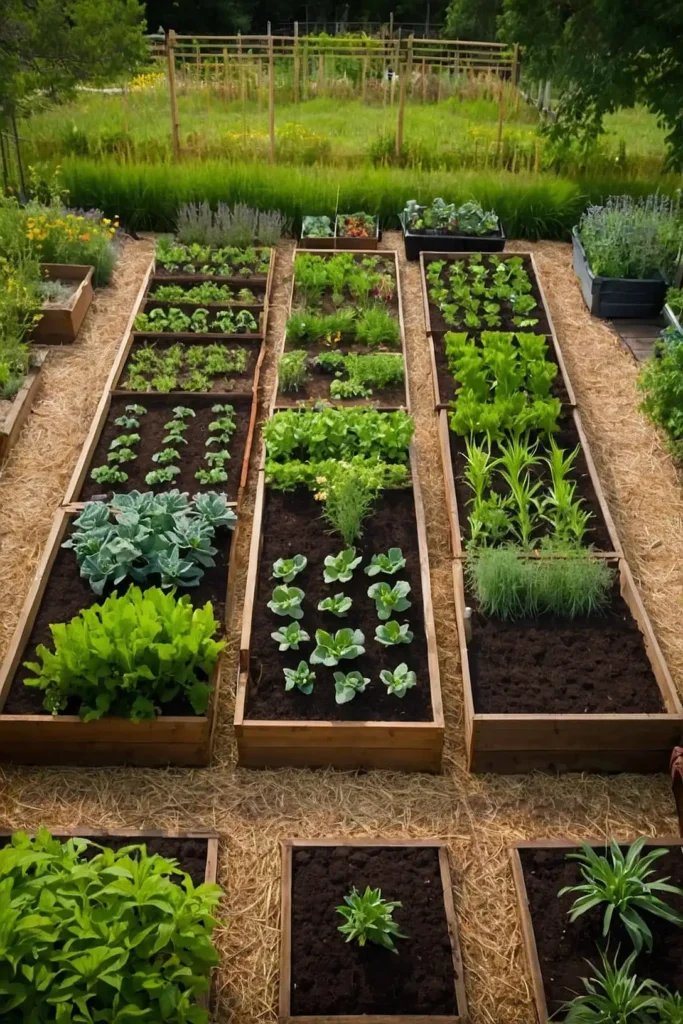

Group compatible plants together in dedicated zones that support each other’s growth while deterring pests naturally.
You’ll create beneficial plant relationships that improve yields while reducing maintenance requirements significantly.
Plant tomatoes with basil, carrots with onions, and beans with corn for classic combinations.
These partnerships improve flavor while providing natural pest control through strategic plant placement.
Design zones based on similar water and nutrient needs for efficient irrigation planning.
The companion approach creates healthier plants while maximizing space utilization throughout your growing areas.
3: Three Sisters Guild Traditional Layout

Plant corn, beans, and squash together using Native American agricultural wisdom that creates mutually beneficial growing relationships.
You’ll establish sustainable polyculture systems that improve soil while maximizing productivity efficiently.
Corn provides support for climbing beans while beans fix nitrogen for heavy-feeding corn.
Squash spreads beneath to suppress weeds while retaining soil moisture throughout the growing season.
Space corn plants 18 inches apart with beans planted around each stalk base.
Add squash plants around the perimeter for complete guild integration and maximum space utilization.
4: Herb Spiral Vertical Efficiency

Build spiraling raised beds that create microclimates for different herbs while maximizing growing space in compact areas.
You’ll accommodate plants with varying water and sun requirements within one integrated structure.
Position Mediterranean herbs at the sunny, well-drained top while placing moisture-loving herbs at the bottom.
This natural arrangement suits plant preferences while creating attractive vertical garden features.
Use stones or logs to create spiral walls that retain heat and provide drainage.
The vertical approach creates more growing surface while adding architectural interest to your homestead garden.
5: Keyhole Garden Circular Design
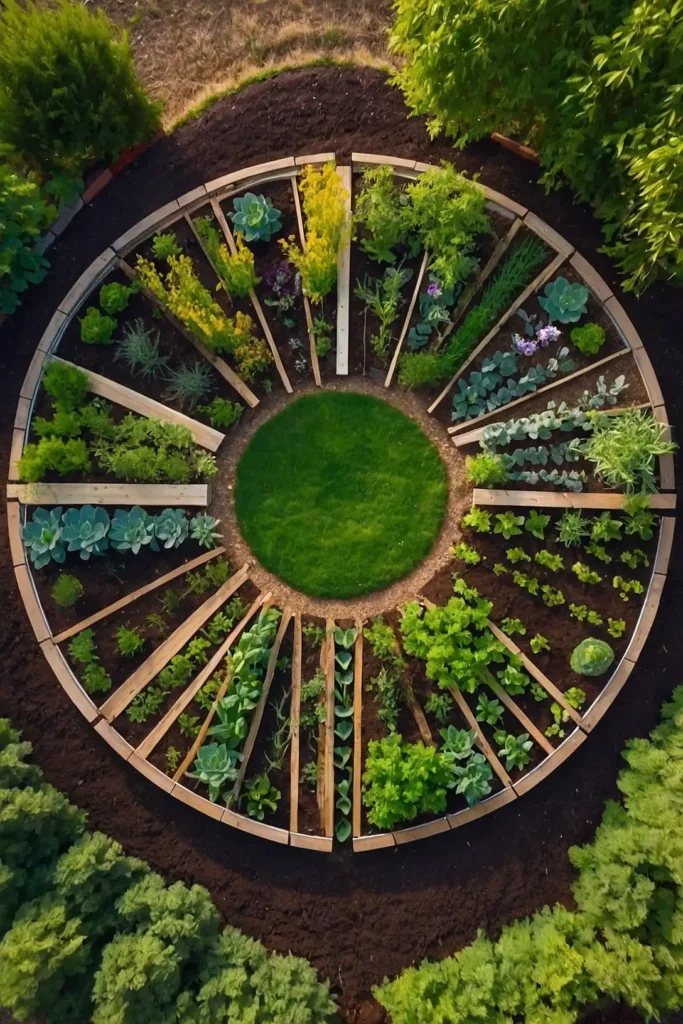

Construct circular raised beds with central compost baskets that provide nutrients while conserving water through efficient design.
You’ll create self-fertilizing systems that require minimal external inputs while maximizing production.
Build beds 6-8 feet in diameter with keyhole-shaped openings for easy access to all areas.
The circular design allows you to reach every plant while maintaining organized growing spaces.
Fill central baskets with kitchen scraps that decompose and feed surrounding plants continuously.
This integrated approach reduces waste while providing steady nutrition for healthy plant growth.
6: Mandala Garden Sacred Geometry
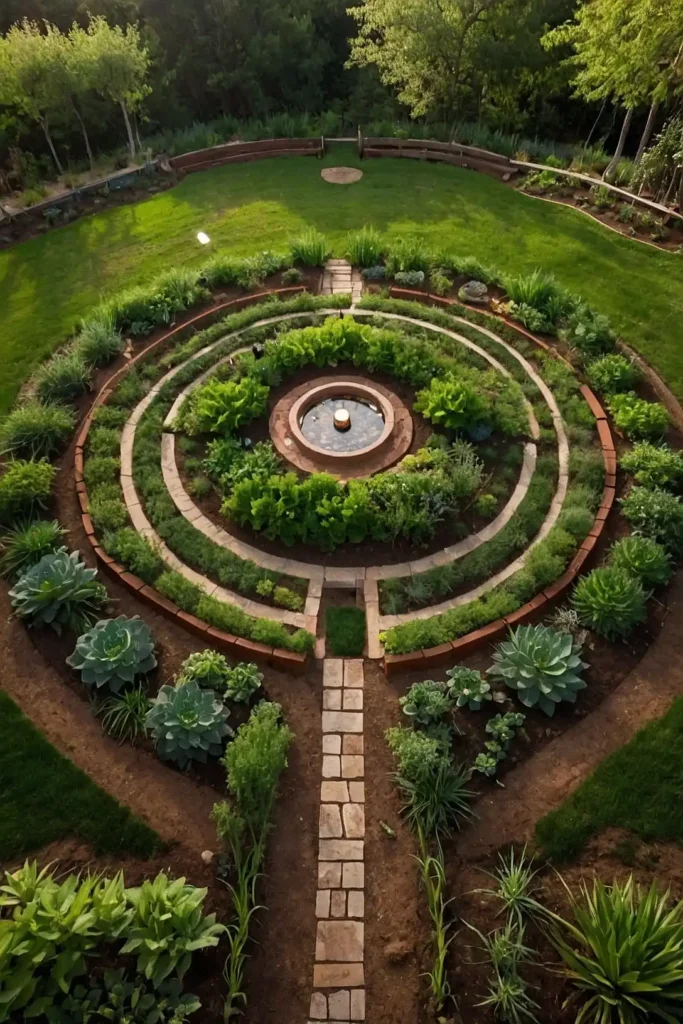

Design circular garden beds arranged in mandala patterns that create beautiful, balanced growing spaces with spiritual significance.
You’ll combine aesthetics with functionality while establishing harmonious garden relationships.
Divide circles into wedge-shaped sections for different plant families or seasonal crops throughout the year.
This organization simplifies crop rotation while creating visually striking garden patterns.
Add pathways between circles for easy maintenance access and meditation walks.
The sacred geometry approach creates peaceful garden spaces while maintaining practical growing functionality.
7: Square Foot Intensive Spacing
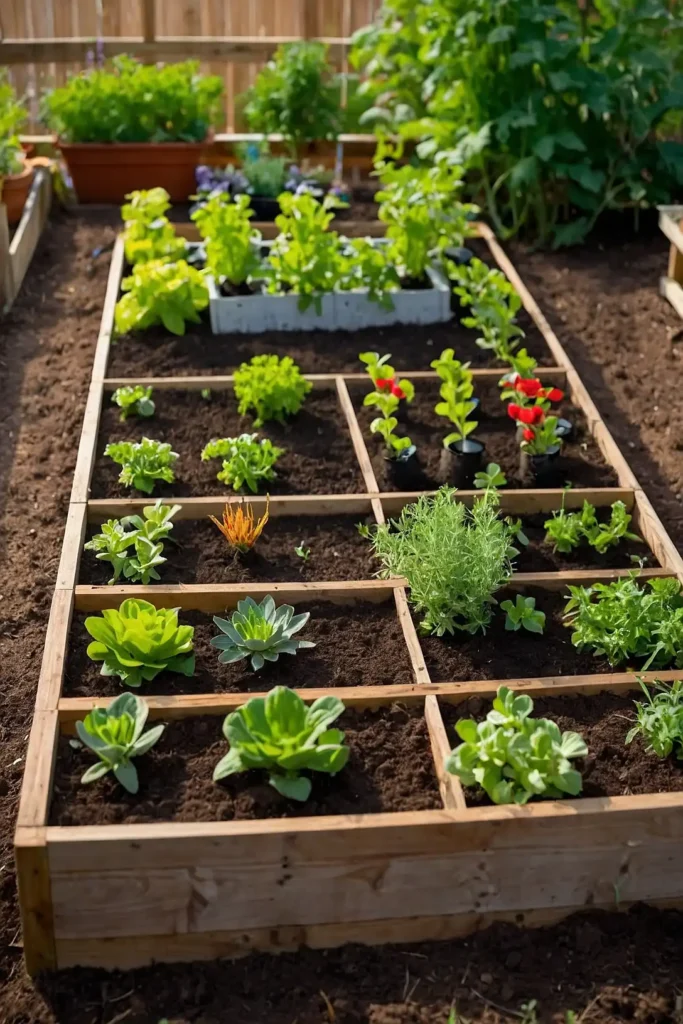

Divide growing beds into square-foot sections that maximize plant density while simplifying spacing and succession planting throughout seasons.
You’ll achieve higher yields from smaller spaces through intensive management techniques.
Plant different vegetables in each square based on mature size requirements and growth habits.
This method prevents overcrowding while ensuring optimal spacing for healthy plant development.
Mark grid lines with string or wood strips for easy section identification and planning.
The systematic approach simplifies record-keeping while maximizing productivity in limited growing space.
8: Permaculture Food Forest Layers
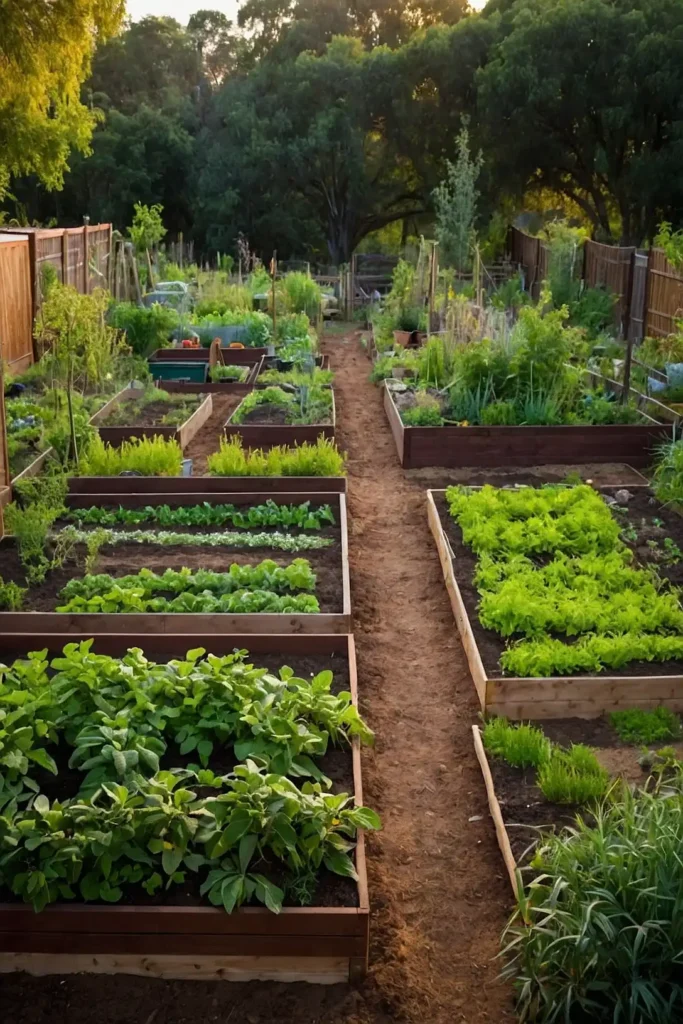

Create multi-level growing systems that mimic forest ecosystems while producing food at different heights throughout your space.
You’ll establish sustainable systems that improve over time while requiring minimal maintenance inputs.
Plant fruit trees as canopy layer with berry bushes, herbs, and ground covers beneath.
Each layer captures different light levels while contributing to overall ecosystem health and productivity.
Include nitrogen-fixing plants throughout all layers to improve soil naturally over time.
The forest approach creates resilient systems while providing diverse harvests from integrated growing spaces.
9: Vertical Growing Tower Systems
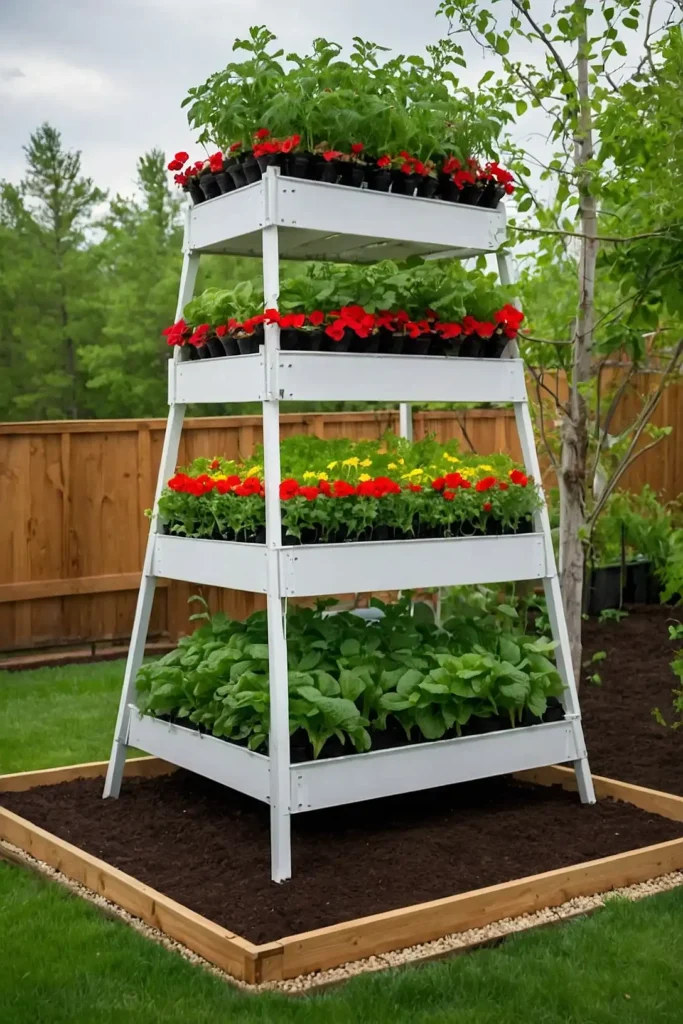

Install vertical growing structures that maximize production in small spaces while providing easy access for maintenance and harvesting.
You’ll grow more food while conserving ground space for other homestead activities.
Use trellises, towers, or hanging systems for vining crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and beans.
These structures support heavy yields while keeping plants organized and accessible for care.
Position vertical elements to avoid shading shorter plants while maximizing sun exposure throughout the day.
The upward approach increases growing capacity while maintaining efficient garden organization.
10: Greenhouse Integration Planning

Position greenhouse structures strategically within your garden layout to extend growing seasons while protecting tender plants from weather extremes.
You’ll achieve year-round production while maintaining integrated garden flow.
Connect greenhouse to water sources and electrical service for automated systems and climate control.
These conveniences improve plant care while reducing daily maintenance requirements significantly.
Plan pathways between greenhouse and outdoor beds for easy transplanting and harvest transport.
The integrated approach creates seamless transitions between protected and open growing areas.
11: Season Extension Hoop Coverage

Install removable hoop houses over beds that extend growing seasons while protecting crops from frost and pests naturally.
You’ll harvest fresh food longer while maintaining flexible garden management options.
Choose lightweight materials that move easily between different beds throughout changing seasons.
This flexibility allows you to protect priority crops while adapting to weather conditions.
Size hoops to accommodate mature plant heights while providing adequate air circulation space.
The protection approach extends harvest periods while maintaining healthy growing conditions for plants.
12: Central Compost System Placement
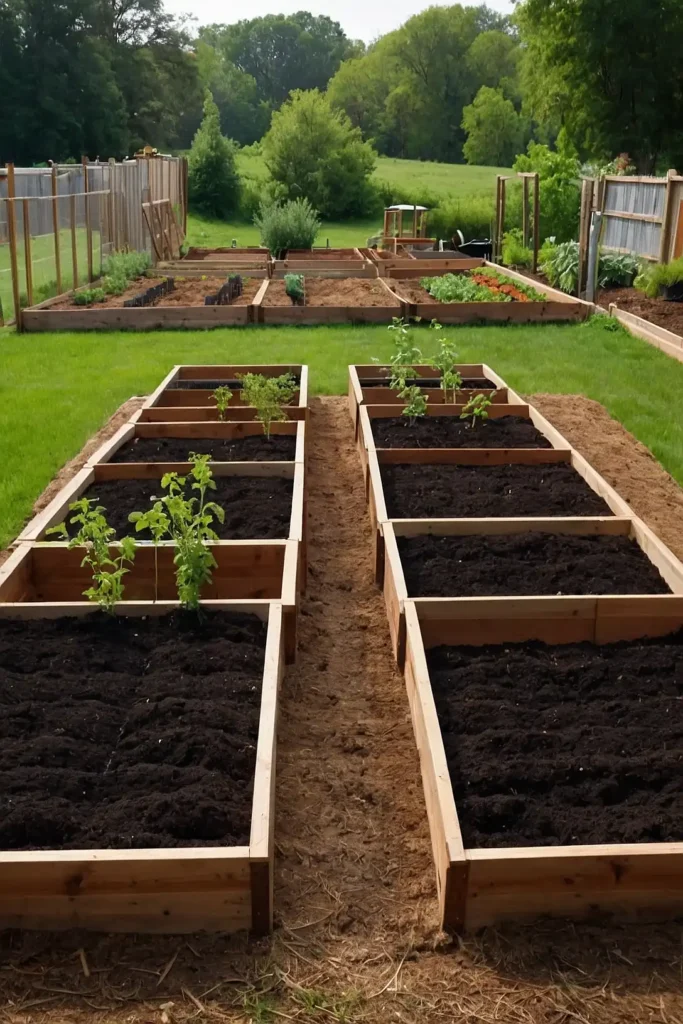

Position compost bins centrally within your garden layout for convenient access while creating nutrient distribution points throughout growing areas.
You’ll reduce transportation while establishing efficient waste processing systems.
Build multiple bins for different decomposition stages from fresh materials to finished compost ready for use.
This rotation system provides steady nutrient supplies while managing organic waste effectively.
Connect compost areas to water sources for moisture management during decomposition processes.
The central location encourages regular use while supporting soil health throughout your entire garden.
13: Rainwater Collection Integration
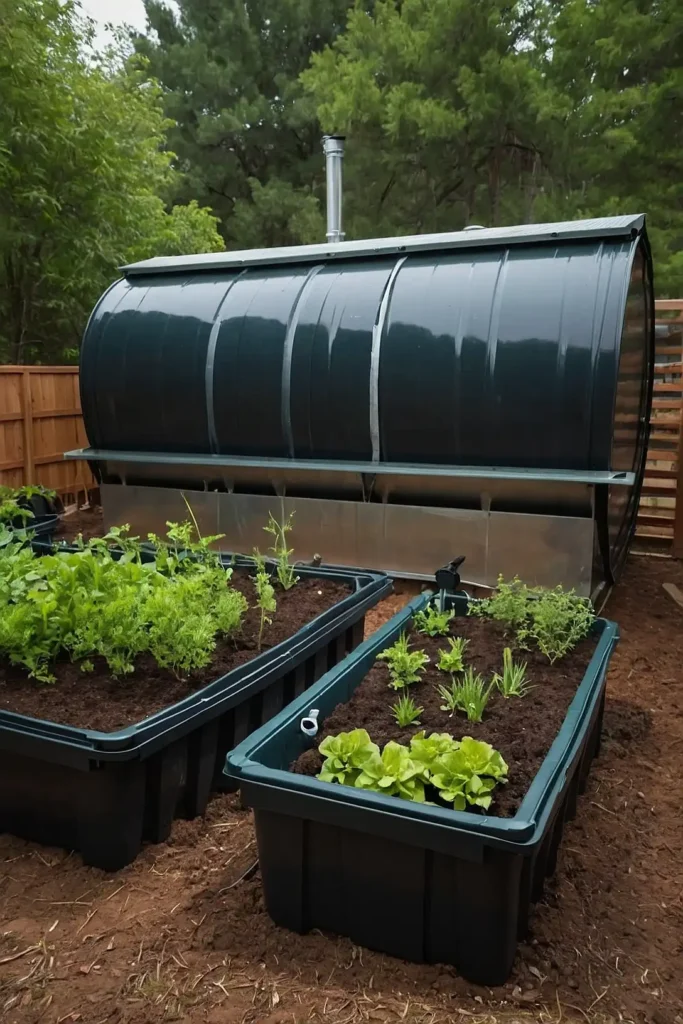

Design garden beds around water collection and distribution systems that capture precipitation while providing irrigation throughout dry periods.
You’ll achieve water independence while supporting consistent plant growth naturally.
Position rain barrels and swales to direct water toward growing areas during heavy rainfall events.
These systems store water while preventing erosion and nutrient loss from garden beds.
Install drip irrigation connected to collected water for efficient plant watering during droughts.
The integrated approach conserves resources while maintaining productive gardens through variable weather conditions.
14: Tool Storage Strategic Positioning
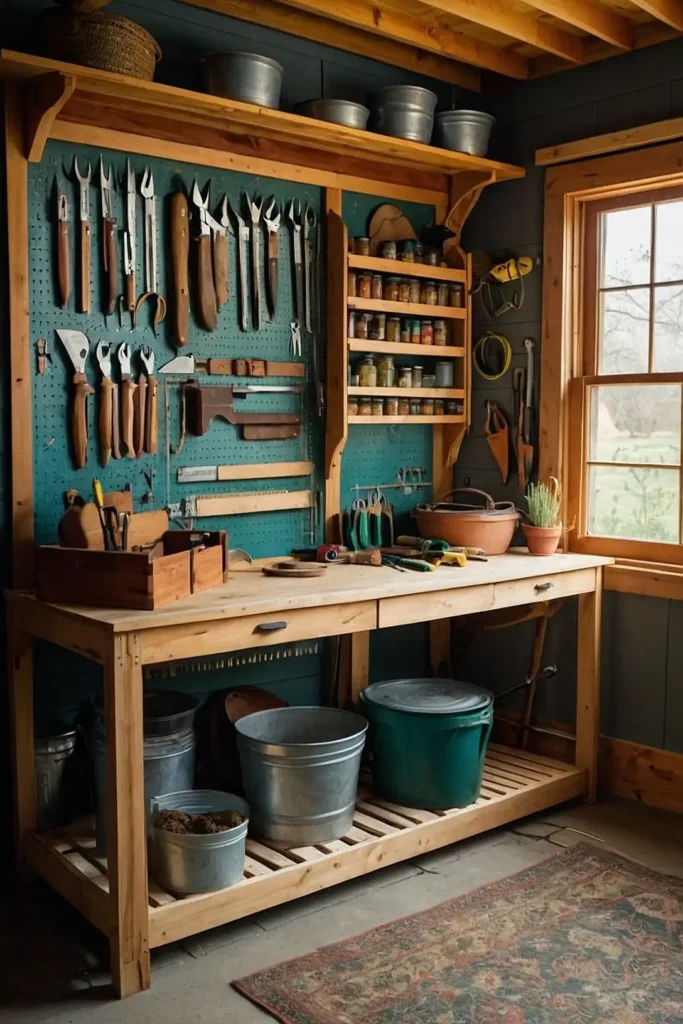

Place tool sheds and storage areas centrally within your garden layout for convenient access while protecting equipment from weather damage.
You’ll improve work efficiency while maintaining organized, accessible garden management systems.
Include workspace areas for seed starting, tool maintenance, and harvest processing near storage locations.
These dedicated spaces improve productivity while keeping garden operations organized and efficient.
Design storage to accommodate different tool sizes while providing easy access during busy seasons.
The strategic placement reduces transportation time while protecting valuable gardening equipment and supplies.
15: Chicken Run Garden Integration
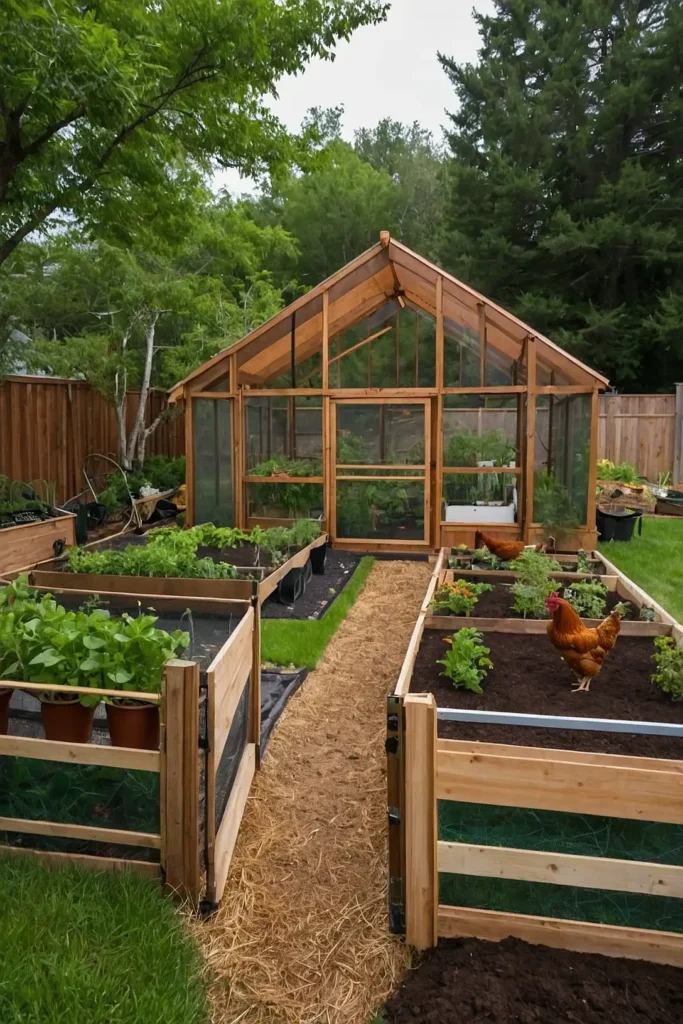

Connect chicken runs to garden areas that provide pest control while adding fertility through natural scratching and fertilizing behaviors.
You’ll create beneficial relationships while maintaining healthy soil and plants.
Rotate chickens through different garden sections seasonally to prevent overuse while distributing benefits evenly.
This management approach maintains soil health while providing consistent pest control throughout growing areas.
Install moveable fencing that allows flexible run positioning while protecting growing crops from damage.
The integration approach supports both poultry and plant health through thoughtful management.
16: Orchard Understory Food Production
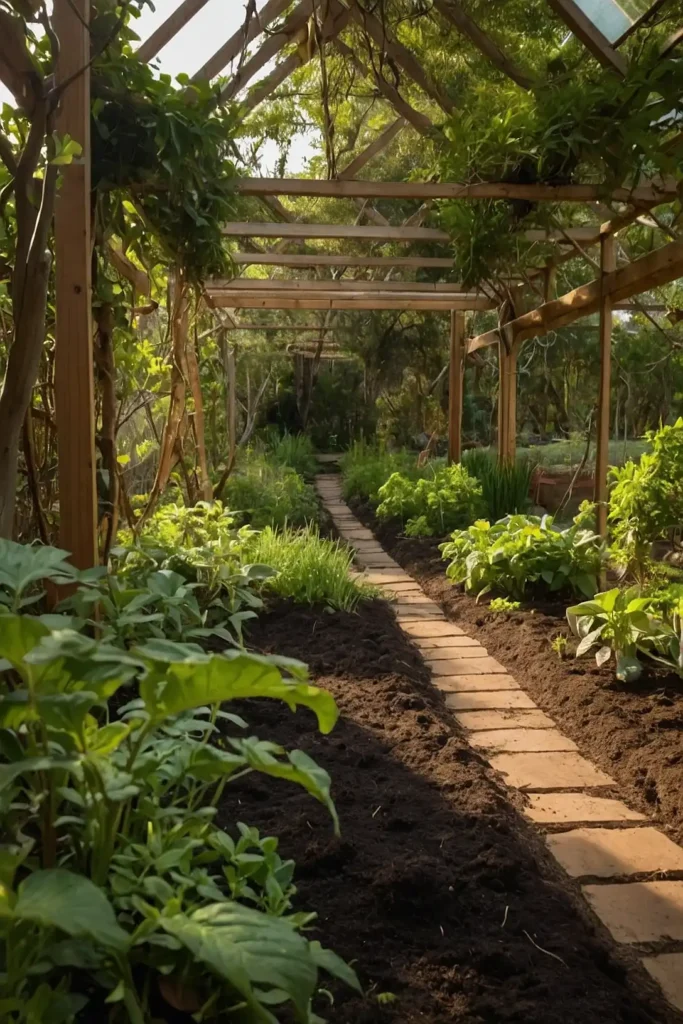

Plant edible ground covers and herbs beneath fruit trees that maximize production while providing beneficial relationships for tree health.
You’ll create layered systems that produce multiple harvests from single areas.
Choose shade-tolerant plants like wild ginger, ramps, or woodland herbs that thrive beneath canopies.
These understory crops add diversity while utilizing space that would otherwise remain unproductive.
Include nitrogen-fixing plants that improve soil while supporting tree health and fruit production.
The layered approach creates forest-like systems while maintaining organized, productive growing spaces.
17: Perennial Border Food Hedgerows
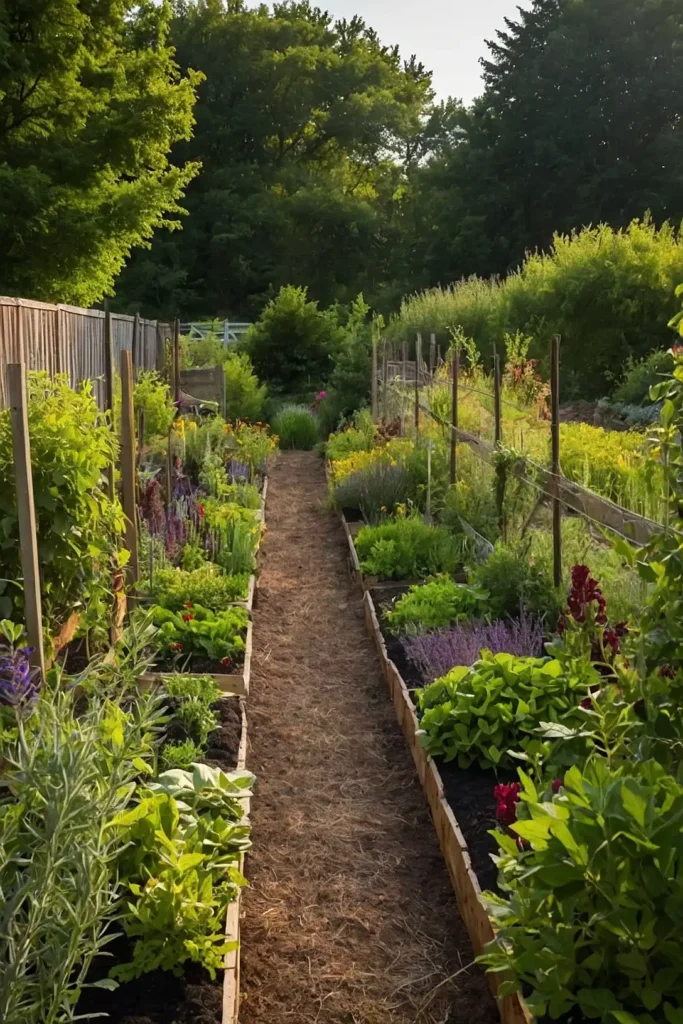

Establish edible perennial borders around your property that provide food while creating natural boundaries and wildlife habitat.
You’ll achieve multiple functions while reducing annual planting and maintenance requirements.
Plant berry bushes, nut trees, and perennial vegetables that produce for many years.
These long-term investments provide steady harvests while establishing permanent garden structure and organization.
Include flowering plants that attract beneficial insects while providing beauty throughout growing seasons.
The border approach creates productive edges while supporting overall garden health and biodiversity.
18: Root Cellar Access Garden Planning
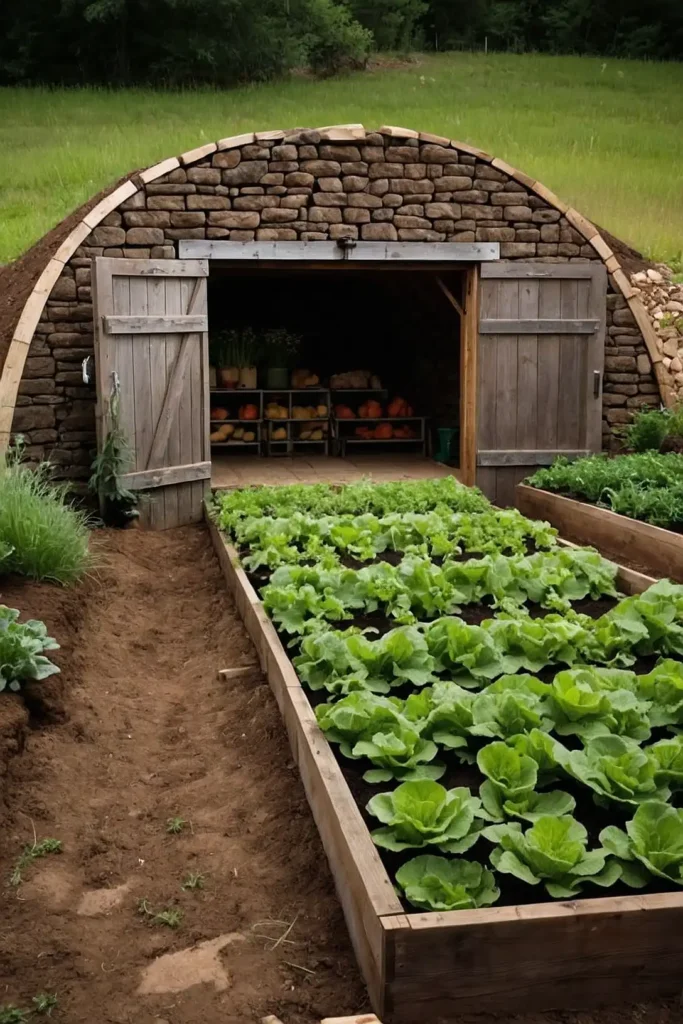

Design growing areas that connect easily to root cellars or storage areas for convenient harvest preservation and storage.
You’ll create efficient systems that support food security while reducing post-harvest transportation.
Plant storage crops like potatoes, carrots, and onions near preservation facilities for easy harvesting.
This proximity reduces handling while maintaining quality during storage preparation and processing.
Include washing and processing areas between garden and storage for efficient harvest workflows.
The connected approach improves food preservation while reducing labor during busy harvest periods.
19: Medicinal Herb Dedicated Zones
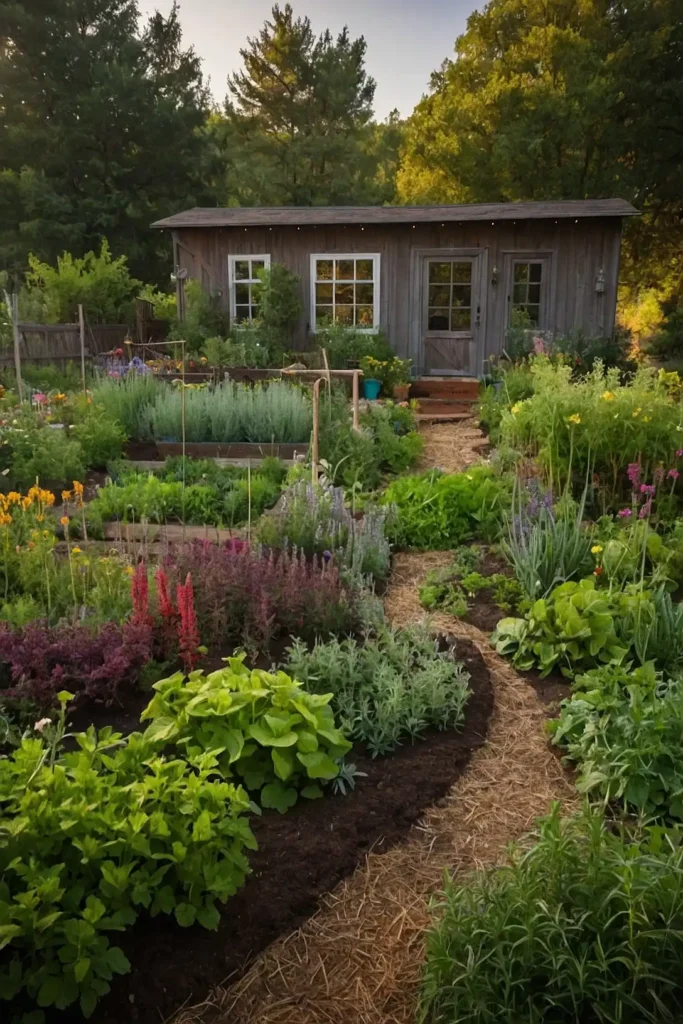

Create separate areas for medicinal plants that require specific growing conditions while keeping healing herbs organized and easily accessible.
You’ll establish pharmacy gardens that support family health while maintaining botanical organization.
Group herbs by medicinal properties or growing requirements for efficient care and harvesting throughout seasons.
This organization simplifies identification while ensuring proper plant care and optimal potency.
Include drying and processing areas near medicinal gardens for convenient herb preparation and storage.
The dedicated approach supports herbal medicine while maintaining organized, accessible healing plant collections.
20: Seed Saving Garden Organization
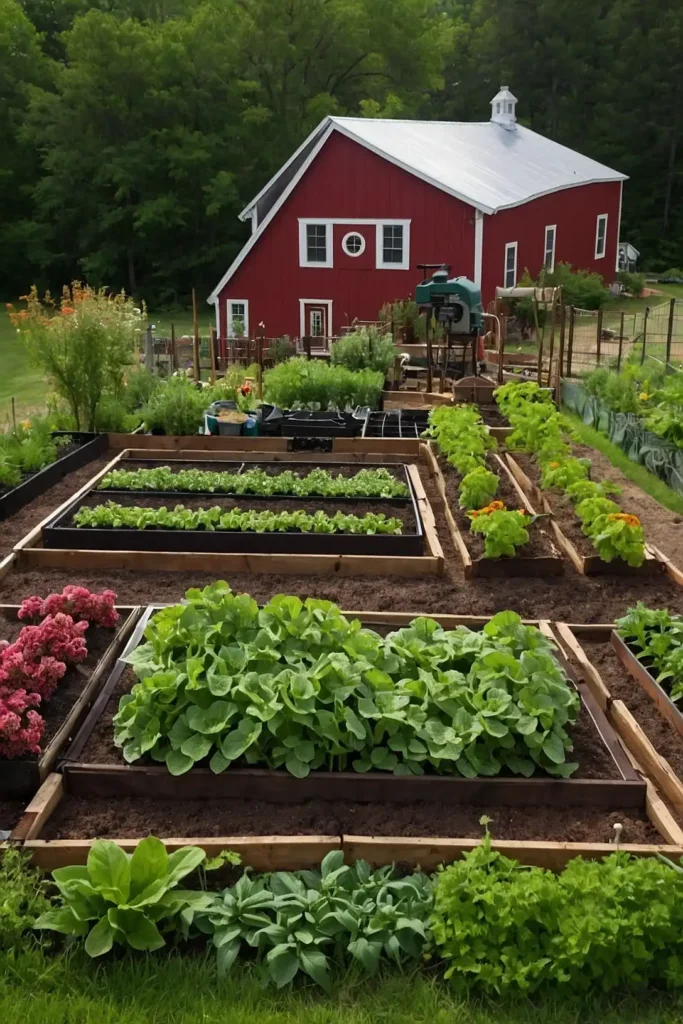

Designate specific areas for plants grown primarily for seed collection that maintains genetic diversity while supporting garden sustainability.
You’ll achieve seed independence while preserving heirloom varieties for future seasons.
Plant seed crops in isolated areas to prevent cross-pollination while maintaining variety purity.
This separation ensures genetic integrity while providing reliable seed sources for continued garden production.
Include drying and storage facilities near seed production areas for efficient harvest processing.
The specialized approach supports seed saving while maintaining organized, sustainable gardening practices.
21: Cut Flower Production Sections
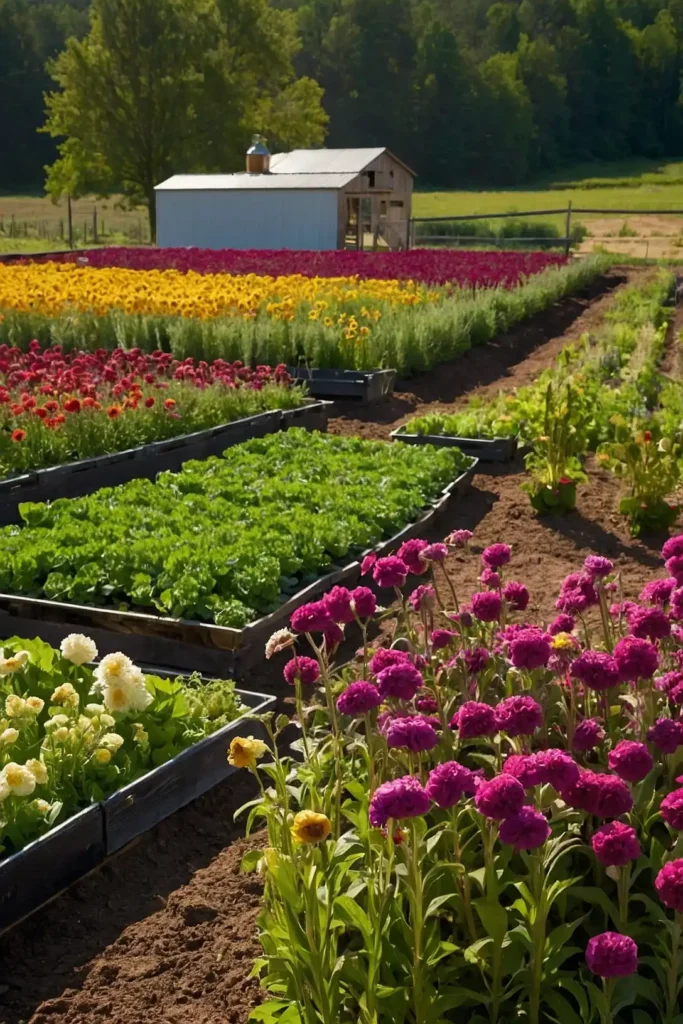

Establish dedicated flower growing areas that provide beauty while supporting beneficial insects and natural pest control throughout your homestead. You’ll create attractive spaces while maintaining productive garden ecosystems.
Plant flowers that bloom throughout seasons for continuous color while supporting pollinator populations year-round.
This succession approach maintains habitat while providing steady flower harvests for home decoration.
Include processing areas for flower arranging and preparation near growing sections.
The dedicated approach supports flower production while maintaining organized, beautiful homestead landscapes.
22: Children’s Learning Garden Spaces
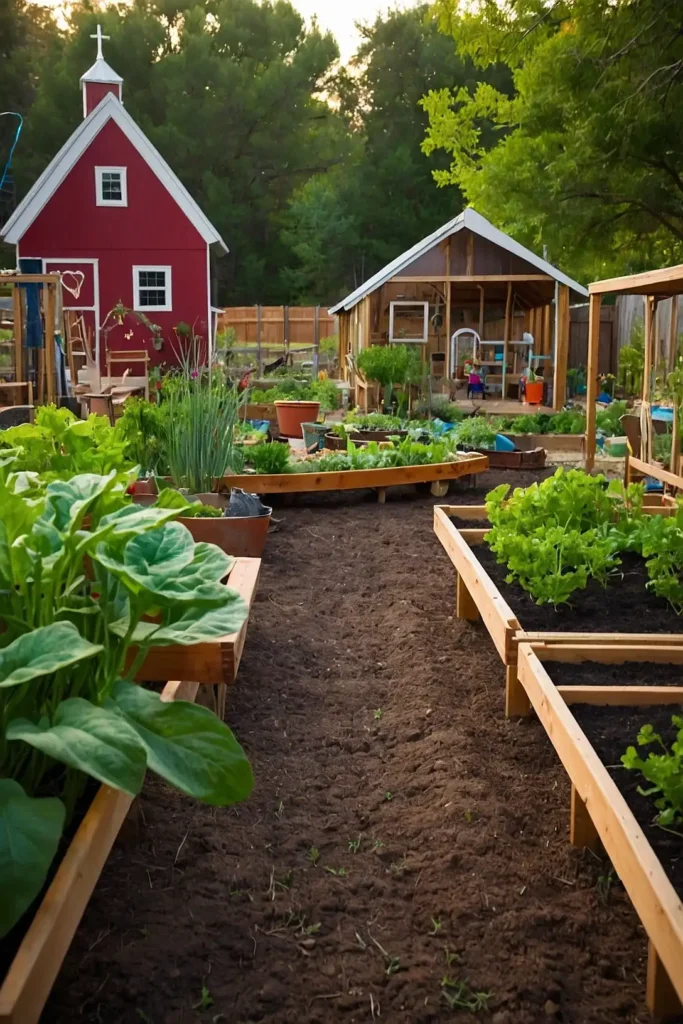

Design child-sized growing areas that encourage family participation while teaching sustainable living skills to younger generations.
You’ll create educational opportunities while maintaining productive, manageable garden spaces for all ages.
Plant easy-growing vegetables like radishes, lettuce, and beans that provide quick results and encourage continued interest.
These reliable crops build confidence while teaching basic gardening principles and plant care.
Include tool storage and seating areas scaled for children’s use and comfort.
The educational approach builds family connections while teaching valuable self-sufficiency skills through hands-on garden experience.
23: Pollinator Habitat Wildlife Zones
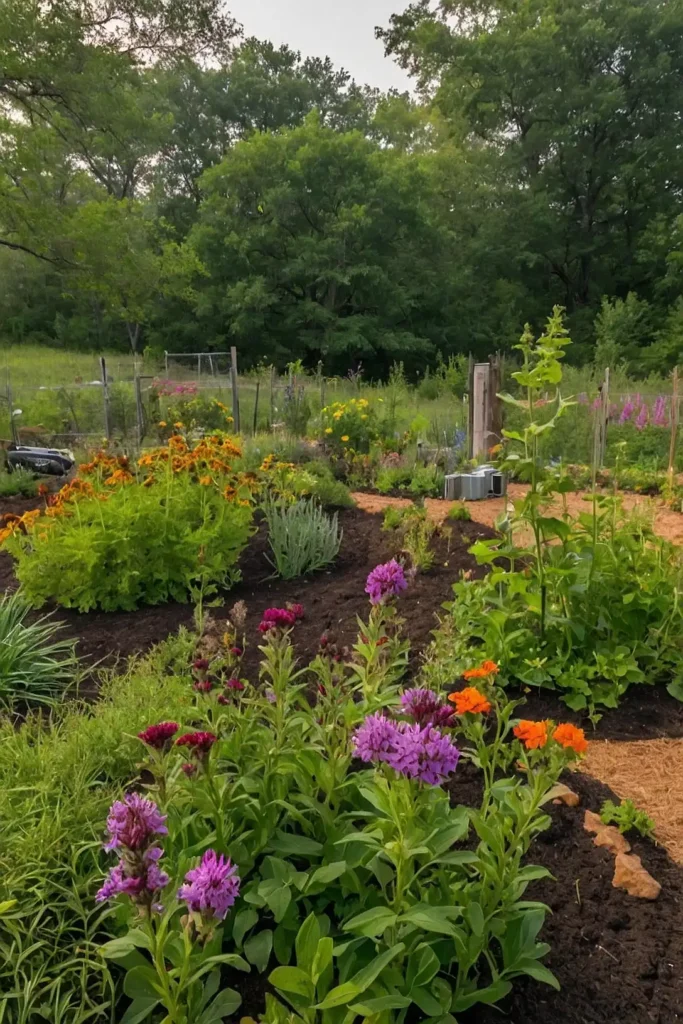

Integrate native flowering plants throughout your garden that support beneficial insects while providing natural pest control and crop pollination.
You’ll create ecological balance while maintaining productive, healthy growing systems.
Plant diverse flowers that bloom throughout seasons for continuous nectar and pollen sources.
This diversity supports various beneficial species while ensuring consistent pollination for food crops.
Include nesting sites and water sources that encourage beneficial insect populations year-round.
The habitat approach creates resilient ecosystems while supporting productive, sustainable homestead gardens.
24: Windbreak Protection Planning

Plant trees and shrubs that protect tender crops from wind damage while creating beneficial microclimates throughout your growing areas.
You’ll improve growing conditions while establishing permanent landscape structure and organization.
Choose plants that provide multiple benefits like fruit, nuts, or firewood while serving as protective barriers.
These productive windbreaks serve dual purposes while contributing to overall homestead productivity and sustainability.
Position windbreaks to protect priority growing areas without creating excessive shade or competition.
The strategic placement improves growing conditions while maintaining optimal light exposure for food crops.
25: Microclimate Zone Utilization

Identify and utilize different microclimates throughout your property that support diverse growing requirements while maximizing production potential.
You’ll match plants to optimal conditions while creating efficient, productive garden systems.
Use warm, protected areas for heat-loving crops while utilizing cool, moist spots for different vegetables.
This matching approach improves plant health while maximizing growing success throughout your property.
Create additional microclimates through strategic structure placement and landscape modification techniques.
The climate approach expands growing possibilities while supporting diverse crop production throughout your homestead.
26: Succession Planting Timeline Layout

Plan garden beds that accommodate sequential plantings throughout seasons while maintaining continuous harvests and optimal space utilization.
You’ll achieve steady food production while maximizing garden productivity through strategic timing.
Plant quick-growing crops like lettuce and radishes every few weeks for continuous harvests.
This timing approach prevents gluts while ensuring steady food supplies throughout growing seasons.
Include fast-maturing varieties that allow multiple plantings in single seasons while maintaining soil health.
The succession approach maximizes productivity while supporting consistent family food security.
27: Four Season Growing Calendar

Design gardens that produce food throughout all seasons while maintaining soil health and garden productivity year-round.
You’ll achieve food security while creating sustainable systems that support continuous family nutrition.
Plan cold-hardy crops for winter harvests while preparing spring planting areas during dormant seasons.
This year-round approach maintains garden productivity while supporting continuous food production and self-sufficiency.
Include season-specific infrastructure like cold frames and row covers that extend growing periods naturally.
The four-season approach maximizes garden potential while supporting year-round homestead food security.
Conclusion
These homesteading garden layouts create productive, sustainable systems that support self-sufficient living while building soil health and family food security beautifully.